How to make the Mediterranean diet more metabolically healthy for you
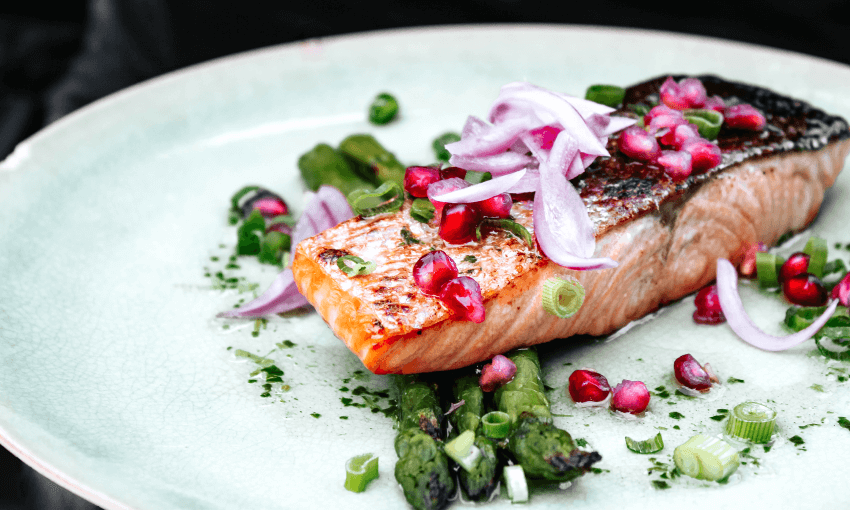
Are you aware that achieving your health goals heavily depends on your metabolic well-being? We advocate for nutritious eating plans that yield enduring outcomes, but customizing these plans with individualized macro strategies can significantly improve your chances of achieving your health targets.
Fast-acting diets may not be suitable for everyone, and maintaining them long-term can be challenging. Diets like these fail to regulate your carb intake, which could potentially backfire as your body loses its ability to process carbs efficiently. Those who follow fast-acting diets often find themselves at a loss. If you're looking for a sustainable, long-lasting diet plan, embracing healthy eating habits is the key. The challenge, however, lies in optimizing your eating plan for metabolic health and your unique physiology.
A recommended strategy for overcoming metabolic syndrome includes integrating positive lifestyle changes and proven interventions into your routine you can boost your metabolism - based mainly on a healthy diet, movement, quality of sleep, and sustainable weight loss. Understanding where your metabolism currently sits is your first step to making healthy changes; take this 1-minute metabolic health assessment to find out.
Creating a flexible metabolism helps your body become strong, healthy, and resilient so you can burn the food you eat for energy, instead of storing it as fat. Plus, it's easier than you might think.
While there are many trendy diets out there, and no one diet is perfect, the Mediterranean diet has stood the test of time and has been research-backed. This dietary approach emphasizes foods traditionally eaten in countries like Greece and Italy, but there are still some fundamental principles you can follow to eat for your metabolism. Let's take a closer look.
The Mediterranean diet is a healthy plant-based diet cooked with traditional flavors and methods of regions around the Mediterranean, such as Italy and Greece. Mediterranean diet recipes became popular when we discovered that people in these regions were extraordinarily healthy and had a lower chance of contracting chronic diseases such as heart diseases, which are more common in other countries like the United States (2).
The Mediterranean diet emphasizes whole, nutrient-rich foods, including fruits, greens, lean protein, whole grains, and healthy fats - all of which have amazing health benefits.
How is that different from what you normally eat? Mediterranean diets are considered healthier than Western diets, often high in processed foods, sugar, and saturated fats.
The problem starts when we consume nutrient-poor foods high in sugar. We trigger a cycle of fluctuations in blood glucose. When our blood glucose drops, it encourages carb snacking, which may lead to weight gain, slow metabolism, and insulin resistance. With this cycle being centered around unhealthy carbs, we can get trapped "in the current".
The Mediterranean diet is healthier because it encourages people to consume whole, nutrient-dense foods that support overall health and well-being rather than processed snacks and fast food. Using a personalized nutritional plan can help you better guide your decisions, especially when you have real-time insights into your metabolic rate.
The foods in the Mediterranean diet are based on high amounts of anti-inflammatory foods, fiber, phytochemicals, and quality fats and proteins. Several studies have shown that this diet leads to a healthier heart, longer life, and healthy weight loss.
"Healthy fats such as those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil can help to support a healthy metabolism. These fats provide essential fatty acids that the body needs to function properly and can help to keep you feeling full and satisfied."
The Mediterranean diet meal plan provides the body with the essential nutrients it needs to function optimally and can help boost energy levels, regulate digestion, and support immune function. For instance, eating fish, a primary source of omega-3 fatty acids, has been linked to improved insulin sensitivity, reduced inflammation, and a lower risk of type 2 diabetes.
Moreover, plants in the Mediterranean diet are rich in antioxidants, which can reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, which are associated with various metabolic disorders. Their high fiber content also helps regulate blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce inflammation - all of which are signs of a healthy metabolism. The diet excludes heavy consumption of red meat, dairy products, excess salt, and carbonated drinks.
Choose: vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, legumes, whole grains, herbs, spices, extra virgin olive oil
Eat these in moderation: chicken, cheese, eggs, and yogurt
Avoid eating: red meat, high-sugar beverages, added sugars, processed meats and snacks, refined oils and grains.
Integrate physical activity: the adoption of healthy lifestyles, which include regular physical activity. Either moderate or vigorous intensity activities may result in longevity benefits, optimizing metabolism, and significantly decreasing the risk of health conditions, among many more benefits.
Share meals with others: Socializing with others might help you minimize stress levels and increase levels of dopamine. Sharing meals may also limit overeating.
It’s not always easy to incorporate a new diet. But here are a few tips from our Lumen nutritionists that can help you to start and stick to the Mediterranean diet long-term:
No one expects you to go full Mediterranean overnight. Start small, perhaps by replacing refined grains with whole grains and adding more vegetables to your meals.
Your morning breath measurement sets you up for the day with a personalized plan to guide your eating decisions. With your nutritional plan, you can assess how much to eat to meet your macros by consuming Mediterranean foods. You will find it easier to wake up in fat burn when consuming the right foods, at the right time.
Whole grains, including barley, whole wheat, and quinoa are rich in fiber and other nutrients that keep you full and satisfied. Fiber-rich foods promote stable glucose levels, which helps deter carb snacking. In turn, less carb snacking allows the body to tap into its reserves for fuel and not store carbs as fat. Over time, your metabolic flexibility and insulin sensitivity will improve and help make it easier to achieve your health goals.
Consuming your healthy complex carbs earlier in the day will give you the energy you need for your activities. When it's time to wind down, have a lighter dinner. This will also help you sleep better and shift to fat burn in the morning.
They’re a healthier alternative to trans fats like margarine and butter. Besides, they taste just as good.
With the Mediterranean diet, real food is emphasized. Knowing a few simple recipes will improve your Mediterranean meal diet plan.
What better way to ensure you stick to a new lifestyle than having others share it with you? They’ll be sure to like it, and this will encourage you to stick with it.
Many restaurant meals are suitable for the Mediterranean diet. Choose whole grains, vegetables, legumes, seafood, and healthy fat. Choose olive oil over butter, and also add vegetables to your order. It’s also key to enjoy your meal and savor it with good company, so choose something that sounds good. Here are some helpful, healthy guidelines and tips for holding on to when eating out.
Not everyone benefits from the same diet. Our metabolism is influenced by a variety of things, including our genetics, health, work schedules, families, cultural customs, and more. Therefore, explore different options until you find a nutritional plan personalized for you.
One good thing about the Mediterranean diet is that it is non-restrictive. So, go ahead and explore. Switching to a new diet can be challenging, so be patient and give yourself time to adjust. Small changes can significantly improve your health and well-being over time.
If you’re looking to adopt the Mediterranean diet, here are some key foods to include in your meals: Olive oil, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, fruits, fish, low-fat dairy products, and moderate alcohol consumption are the main components of this diet with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effect. Opt for nutrient-dense foods as much as possible, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, legumes, and whole grains.
Incorporating fruits into your diet is an excellent way to boost your metabolism. Fruits contain a truckload of essential nutrients which are essential for optimal metabolism. Fruits are also a great source of dietary fiber, which helps to improve your digestion and promote feelings of fullness. What’s more? Fruits are also low in calories, so make them an incredible choice for weight loss.
Vegetables can support a healthy metabolism by providing essential nutrients, boosting fiber intake, and supporting detoxification. Besides, most vegetables are low in calories, so they help reduce your calorie intake and support your weight loss.
Adding legumes to your diet is a simple and delicious way to support a healthy metabolism. Legumes are an excellent source of plant-based protein, dietary fiber intake, complex carbohydrates, and other essential nutrients. The fiber helps to improve digestion, the plant-based protein helps build muscle mass and the complex carbohydrate provide a stable source of energy for the body - all of which improve your body’s metabolism.
Whole grains can promote a healthy metabolism by providing fiber, complex carbohydrates, B vitamins, and essential minerals. For example, whole grains are a rich source of essential minerals such as iron, magnesium, and zinc, crucial for healthy metabolic function. Whole grains also provide B vitamins such as thiamine, riboflavin, and niacin, essential for energy production and metabolic function.
Nuts aren’t just tasty foods, they can work wonders for your metabolic health. Nuts and seeds are excellent sources of heart-healthy fats, fiber, plant protein, and essential vitamins and minerals. The healthy fats can help reduce inflammation, improve cholesterol levels, and support heart health, which is essential for overall metabolic function. Nuts and seeds are also a great source of dietary fiber, which can help improve digestion, regulate blood sugar levels, and promote feelings of fullness.
Animal products are one of the best sources of high-quality protein, and other essential nutrients, including iron, vitamin B12, and zinc, which are crucial for metabolic function. Top tip: Although animal products provide an excellent way to improve your metabolism, eating too many animal products high in saturated and trans fats can increase your risk of metabolic disorders such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
Seafood is a delightful and healthy source of protein with less fat and cholesterol compared to other types of meat. Protein also has a high thermic effect, meaning that your body uses more energy to digest and metabolize proteins compared to carbohydrates or fats. This can help boost your metabolism and increase calorie burn. Seafood is also incredibly low in calories, making it an excellent diet choice if you want to lose weight.
Healthful fats are incredibly beneficial in supporting a healthy metabolism, improving hormone regulation, boosting energy production, and promoting your overall well-being. Consuming healthy fats in a personalized macro diet will keep you on track. Healthy fats can also keep you feeling full and satisfied for longer periods of time - This can help reduce cravings and prevent overeating, which can contribute to weight gain and metabolic problems.
Water should be your go-to beverage, but others fit this diet plan too. Whether you enjoy it black, iced or with cream, you can still enjoy your delicious cup of coffee and get immense health benefits. It turns out, coffee is one of the most popular Mediterranean drinks. Several studies have found that coffee can improve metabolic rate and increase insulin sensitivity, which can help regulate blood sugar levels and prevent metabolic problems such as type 2 diabetes.
Another popular Mediterranean beverage you can enjoy is a glass of red wine (but drink responsibly), which contains resveratrol, a compound that has been found to help improve metabolic function and reduce inflammation.
Mediterranean cultures also enjoy tea and herbal infusions. Green tea, in particular, has been found to help increase metabolic rate and promote fat oxidation, making it a great choice for those looking to lose weight and promote a healthy metabolism.
Herbal infusions such as chamomile and peppermint can also have a calming effect on the digestive system, promoting healthy digestion and metabolism.
One good thing about the Mediterranean diet is that it is non-restrictive. So, go ahead and explore. Remember, switching to a new diet can be challenging, so be patient and give yourself time to adjust. Small changes can significantly improve your health and wellbeing over time.
Without a doubt, the Mediterranean diet is an absolute gem. Its numerous health benefits make it almost too good to be true. It helps boost your metabolism, help you lose those extra pounds, and reduces the risks of cardiovascular diseases, chronic illnesses, and inflammation. By incorporating these foods into your diet, you can enjoy delicious and nutritious recipes that support overall health and well-being.
Yes, rice can be part of a Mediterranean diet, particularly if it is whole-grain rice such as brown rice.
Whole grain rice like brown rice provides more fiber and nutrients compared to white rice, because it contains the bran and germ of the grain. These components are removed in the process of making white rice, which makes it less nutritious.
Rice is often used in Mediterranean dishes. It can be used in salads, as a side dish, or in pilafs combined with various vegetables and herbs.
That being said, moderation is key, as with all foods, because even healthy foods can contribute to weight gain and other health issues if consumed in excess.
Papadaki, A., & Mantzoros, C. S. (2020). The Effect of the Mediterranean Diet on Metabolic Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Controlled Trials in Adults. Nutrients, 12(11), 3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113342
Grundy, S. M. (2008). Metabolic Syndrome Pandemic. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology., (2008;28:629–636). https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.151092
Caprara, G. (2021). Mediterranean-Type Dietary Pattern and Physical Activity: The Winning Combination to Counteract the Rising Burden of Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs). Nutrients, 13(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020429
Martinez-Gonzalez, M. A., Martin-Calvo, N., & Mediterranean Diet Foundation Expert Group. (2019). Mediterranean diet and life expectancy; beyond olive oil, fruits, and vegetables. Current opinion in clinical nutrition and metabolic care, 22(6), 417-422.
Sofi, F., Cesari, F., Abbate, R., Gensini, G. F., & Casini, A. (2008). Adherence to Mediterranean diet and health status: a meta-analysis. Bmj, 337, a1344.

Our Lumen editorial desk includes an in-house team of certified and registered nutritionists and dietitians, scientists, researchers, and writers.